How to Choose Between DDoS-Protected CDN and DDoS-Protected Servers for China? A Practical Guide
What's the real difference between a DDoS-protected CDN and a DDoS-protected server for China? This guide breaks down their defense principles, DDoS scrubbing methods, CC attack protection, costs, and ideal use cases. Learn the pros, cons, and how to combine them for a truly resilient, fast, and attack-resistant setup.

Many websites aren't killed by the attack itself, but by choosing the wrong protection strategy.
When a website faces its first DDoS or CC attack, most site owners are forced to learn about two terms: DDoS-protected CDN and DDoS-protected server.
The problem is, sales reps often describe them as "pretty much the same," but in real-world scenarios, they play completely different roles.
This article doesn't take sides with any vendor. Instead, from a practical site owner's perspective, we'll clearly explain the fundamental differences, best use cases, and the most reliable combination strategies for DDoS-protected CDNs in China and DDoS-protected servers.
Contents
- 1. What is a DDoS-Protected CDN?
- 2. What is a DDoS-Protected Server?
- 3. Core Differences: Protected CDN vs. Protected Server
- 4. How to Choose for Different Scenarios
- 5. Why More Site Owners Are Choosing Hybrid Solutions
- 6. Practical Checklist for Tech Teams
- 7. Stop Paying for "Fake" Protection
- 8. FAQ
1. What is a DDoS-Protected CDN?
A DDoS-protected CDN is essentially a combination of CDN acceleration + edge traffic scrubbing.
When a user visits your site, the request doesn't go directly to your origin server. Instead, it first hits a CDN edge node, which handles the following:
- Caches static content to reduce origin load
- Identifies and scrubs DDoS traffic at the edge
- Detects CC attacks using behavioral models
- Blocks malicious requests to protect the origin
The biggest advantage of a DDoS-protected CDN is this: Attacks are weakened or completely blocked before they ever reach your server.
Primary Goal:
Scrub malicious traffic at the CDN edge before it hits your origin server.
This is why many sites see a noticeable drop in server load and improved stability after deploying a protected CDN.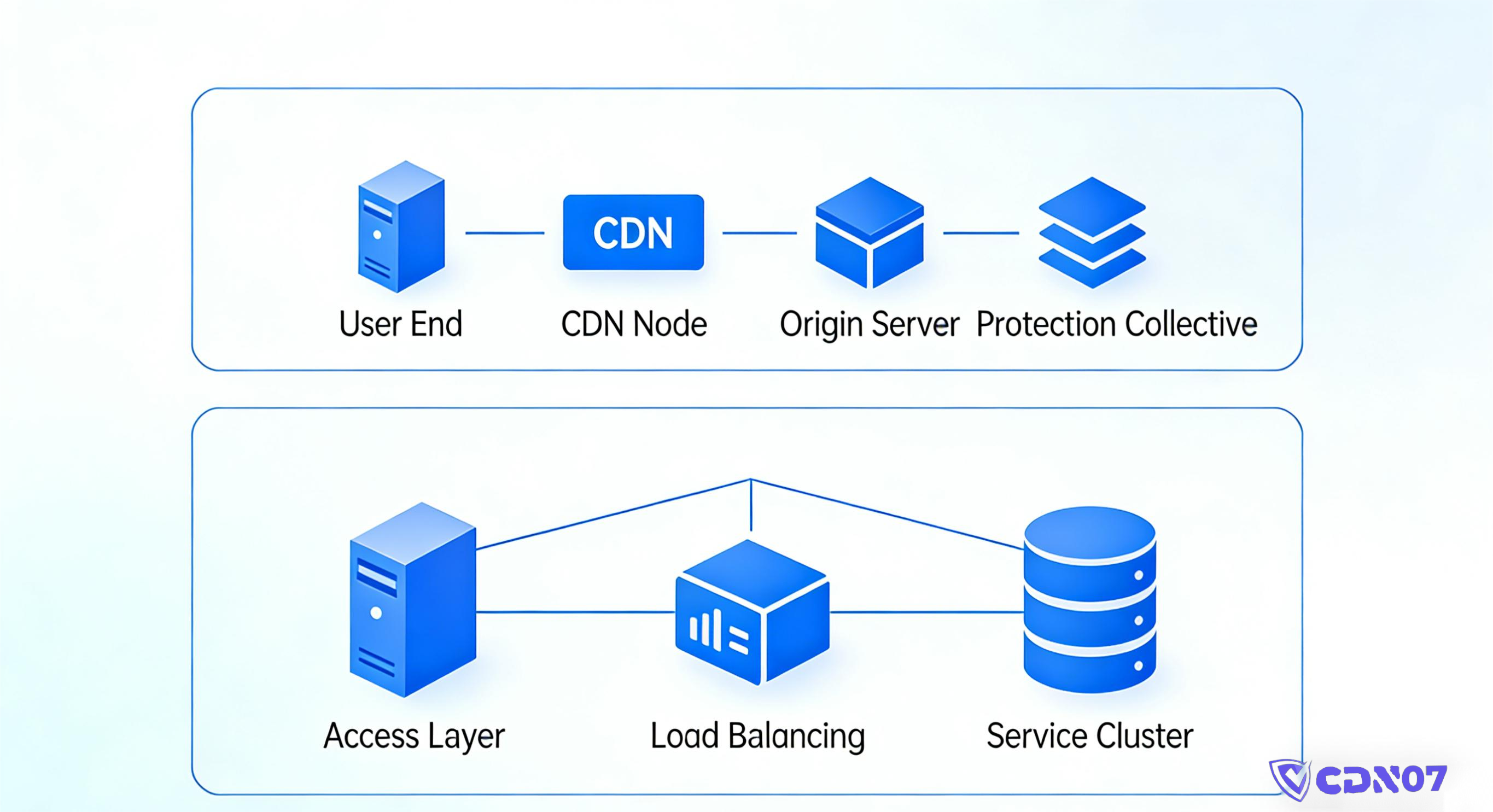
2. What is a DDoS-Protected Server?
A DDoS-protected server typically refers to a server or cluster with high bandwidth and dedicated scrubbing capacity that also hosts your applications.
Unlike a protected CDN, a protected server has these characteristics:
- Your applications run directly on it
- Attack traffic eventually lands at its data center
- It relies on data center-level scrubbing equipment for protection
Think of a DDoS-protected server as your "last line of defense."
Primary Goal:
Locally absorb and scrub attacks + host your core services.
Its strength is handling massive traffic volumes, but it doesn't distribute user access or provide global/regional acceleration.
3. Core Differences: Protected CDN vs. Protected Server
| Comparison | DDoS-Protected CDN | DDoS-Protected Server |
|---|---|---|
| Defense Location | Network Edge Nodes | Server / Data Center Side |
| Provides Acceleration | Yes | No |
| Protection Method | Distributed Scrubbing | Centralized Scrubbing |
| Handles Traffic Spikes | Excellent | Limited Capacity |
| Operational Complexity | Low | High |
In a nutshell: A protected CDN is best as your outer shield, while a protected server is your safety net.
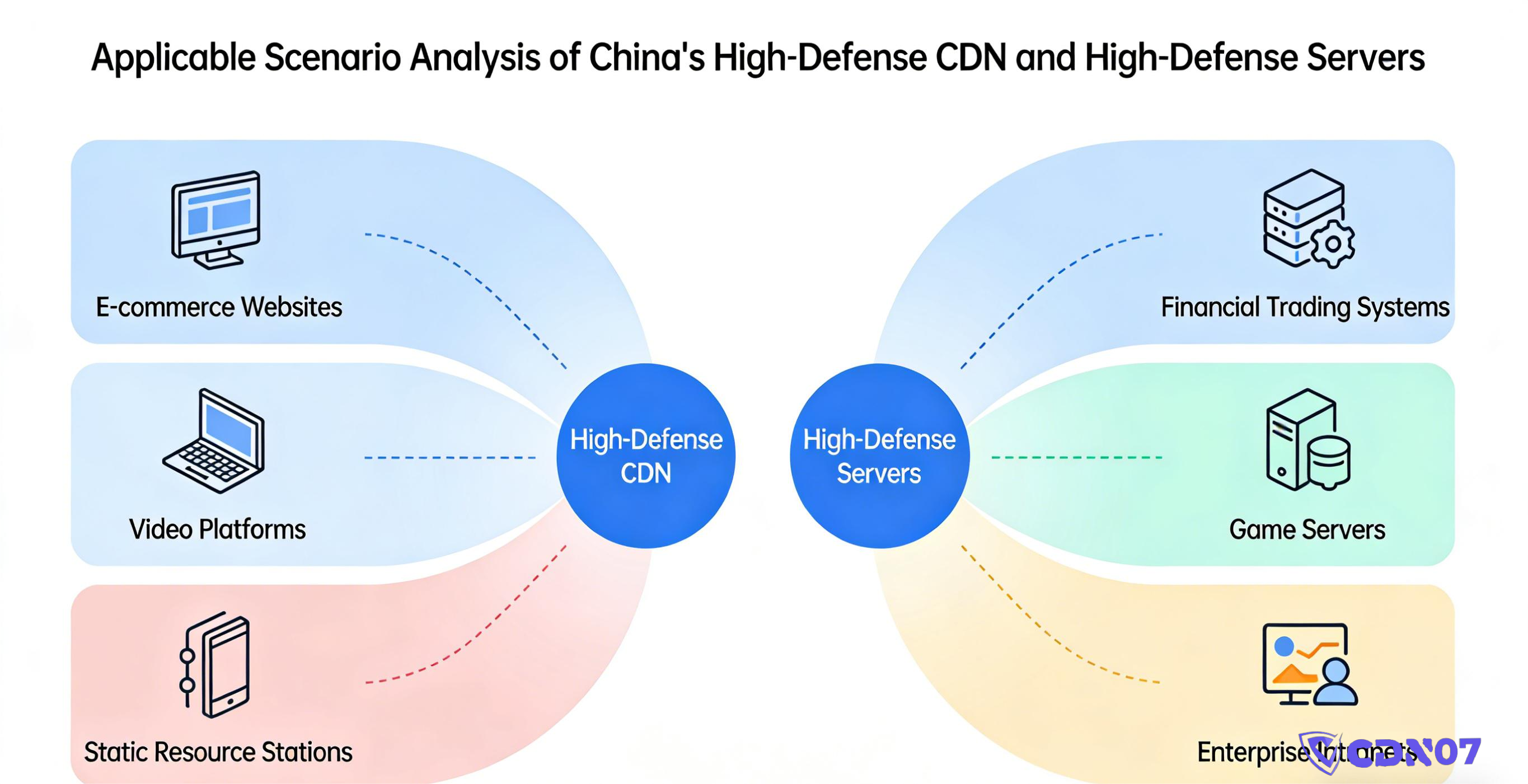
4. How to Choose for Different Scenarios
1. Content Sites / Corporate Websites
These sites don't require extreme real-time performance but are very vulnerable to being crippled by attacks.
Recommendation: A protected CDN is usually sufficient. Prioritize node quality within China and effective CC protection.
2. Cross-Border E-commerce / API Services
Access stability directly impacts conversions and operations.
Recommendation: Protected CDN + application-layer security (WAF). Consider adding a protected server at the origin for critical backup.
3. Gaming / Real-Time Communication
Latency-sensitive and frequently targeted.
Recommendation: Use a protected CDN to block traffic floods, and a protected server to host the core game/chat logic.
How to Choose? A Step-by-Step Process
Here's a practical, actionable selection workflow based on years of experience:
🧩 Step 1: Assess Your Attack Risk Level
Use this table to gauge your risk:
| Site Type | Attack Probability | Business Criticality |
|---|---|---|
| Landing / Promo Pages | High | High |
| API Services | High | High |
| Content / News Sites | Medium | Medium |
| Static Brochure Sites | Low | Low |
🧩 Step 2: Match Defense to Risk
| Attack Risk | Recommended Setup | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| High | Protected CDN + Protected Server | Maximum Resilience |
| Medium | Protected CDN + WAF | Balanced Strategy |
| Low | Protected CDN | Most Cost-Effective |
🧩 Step 3: Consider Access Requirements
If access speed matters:
✅ Main audience in China → Prioritize a China-optimized protected CDN with premium CN2/BGP routes.
✅ Audience in China + globally → Choose a protected CDN with Anycast + China-optimized nodes.
5. Why More Site Owners Are Choosing Hybrid Solutions
In practice, using only a protected CDN or only a protected server has clear weaknesses.
The following architecture is currently the most recommended in the industry:
📌 Benefits of this logic:
- Attacks are weakened at the edge
- Minimal application layer exposure
- Protected server only receives clean traffic
- Reduces origin server CPU / bandwidth pressure
Cost Considerations
Comparison:
| Solution | Cost | Protection Strength | Access Performance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Protected CDN Only | Low ~ Medium | Medium ~ High | High |
| Protected Server Only | High | High | Low (No Acceleration) |
| Hybrid Solution | High | Highest | Highest |
👉 Conclusion: The hybrid setup is the most expensive but also the most stable. A standalone protected CDN is the best value for getting started.
6. Practical Checklist for Tech Teams
📌 CDN Side
- Supports CN2 / BGP / Anycast routing?
- Provides real-time scrubbing logs?
- Automatically handles CC + HTTP Flood attacks?
- Has a false-positive whitelist mechanism?
📌 WAF
- Can you write custom rules?
- Supports ML-based behavioral analysis?
- Integrates with RASP?
📌 Protected Server
- Proof of peak scrubbing capacity?
- Clear SLA guarantees?
- Provides granular log analysis?
7. Stop Paying for "Fake" Protection
DDoS-protected CDNs and servers aren't mutually exclusive; they are complementary security components with different roles.
Choosing the right combination is more important than just picking the "most expensive" option. Truly stable websites are built on a well-thought-out protection architecture from the start.
8. FAQ
Q1: What's the biggest difference between a protected CDN and a regular CDN? A: A regular CDN mainly solves speed issues. A protected CDN adds real-time scrubbing for DDoS and CC attacks. A regular CDN might fail under a large attack, while a protected CDN's core value is "keeping your site accessible during an attack."
Q2: Can I just use a protected server without a CDN? A: Yes, but it's riskier. A protected server is your last line of defense; attack traffic still hits your data center, potentially saturating bandwidth/resources. Without a CDN to filter traffic, server stress increases, making it less stable than a combined setup.
Q3: Can a protected CDN stop all DDoS attacks? A: Nothing is "100%," but it can handle most common attacks like UDP Flood, SYN Flood, HTTP Flood. The real difference lies in the maturity of the scrubbing policies and the ability to quickly distinguish real users from attack traffic.
Q4: Why are CC attacks harder to stop than volumetric attacks? A: CC attacks mimic legitimate user requests, consuming server resources slowly and steadily. Simple rate-limiting isn't enough. Effective protection requires behavioral analysis, access pattern modeling, and WAF rules.
Q5: Does a protected CDN slow down real users? A: A properly configured protected CDN should make your site faster under normal conditions. It only affects users if policies are misconfigured or false-positives are high—something to check when choosing a provider.
Q6: For China-focused business, must I use a China-optimized protected CDN? A: Yes. Users in China are highly sensitive to network routes and node quality. Global protected CDNs might have strong defenses but often suffer from high latency and instability from within China. They're better as a supplement. Alternatively, consider a Hong Kong-based CDN that doesn't require ICP filing.
Q7: How big of an attack can a protected CDN handle? A> It depends on the provider's scrubbing capacity and architecture—some handle hundreds of Gbps, others Tbps+. Note: "shared scrubbing" and "dedicated scrubbing" are very different; don't just look at the advertised numbers.
Q8: Do small/medium sites need a protected server from the start? A> Usually not. Most SMB sites can solve their problems with just a protected CDN. A protected server is better for frequently attacked, highly sensitive, or latency-critical applications.
Q9: Do I need all three: CDN + WAF + Protected Server? A> Not necessarily. The need for three layers depends on business value and attack frequency. For critical operations, it's the safest bet. For typical sites, a protected CDN is often enough.
Q10: How can I tell if a "protected CDN" is legit? A> Check three things: 1) Does it have real scrubbing centers? 2) Does it demonstrably mitigate attacks when they happen? 3) Can it provide attack logs and protection details? Vendors that only talk specs and not real-world performance are likely selling "fake" protection.
Share this post:
Related Posts
A Systematic Approach to Fixing Slow China Access for Overseas Websites
If your overseas site loads slowly in China, the problem usually isn't your server. This guide expla...

The 2026 Guide to DDoS-Protected CDNs: Don't Get Blinded by the Numbers
Looking at specs alone is a trap. This guide breaks down how to choose a DDoS-protected CDN in 2026...

Hong Kong High-Defense CDN Recommendations (2026 Latest Edition)
Not all Hong Kong high-defense CDNs can withstand attacks. This article compares the protection stre...
