Unregistered CDN vs Domestic CDN: Key Differences & Use Cases Explained
Discover core differences between unregistered CDN and domestic CDN – registration rules, node locations, speed, content review, and anti-blocking. Choose the best website acceleration for legit projects, gaming content, overseas promotion, or temporary sites. Avoid pitfalls and make smart choices! Ideal for webmasters & beginners.
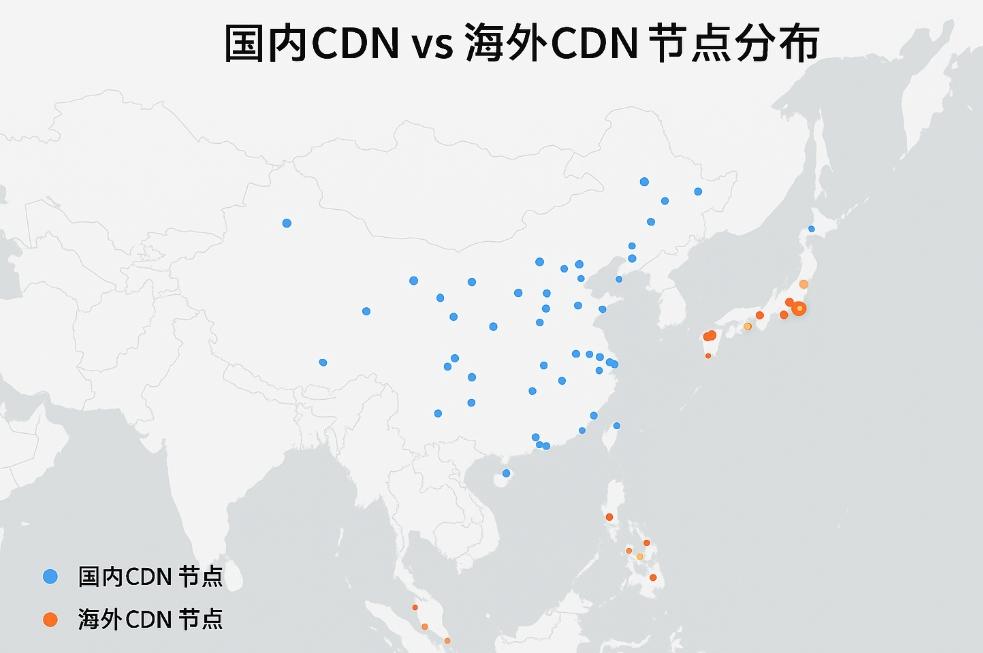
In the internet community, the term "CDN" is frequently mentioned. It affects whether your website loads smoothly or gets stuck, whether your site can handle a sudden surge in traffic, and even whether you will be "blocked" by the Great Firewall.
Today, we are going to talk about two commonly confused CDNs: Non-Filing CDN and Domestic CDN.
What exactly are the differences between them? Who is each one suitable for? Could you make a mistake by choosing the wrong one?
Don’t worry. In this article, I will clarify everything step by step, explaining the basic principles and practical usage scenarios, so you can fully understand the differences between these two types of CDNs.
Table of Contents:
- 1. What is CDN? Let’s clarify that first
- 2. Non-Filing CDN VS Domestic CDN: What’s the difference?
- 3. Why do so many people choose Non-Filing CDN?
- 4. Does Non-Filing CDN have no drawbacks?
- 5. Real-world usage examples: Which one is right for whom?
- 6. Technical comparison summary table
- 7. How to choose a reliable Non-Filing CDN provider?
- 8. Choosing the right CDN is choosing your website’s lifeline
1. What is CDN? Let’s clarify that first
CDN, short for Content Delivery Network, is a network for distributing content.
In simple terms: it doesn’t just deliver your website content from one place, but copies it and places it in multiple server nodes across the country or even the world. This way, users can access content from the nearest server, improving speed and stability.
Imagine opening a restaurant with only one branch in Beijing. People from all over the country would have to come to Beijing to eat, which is slow. CDN is like opening branches in every province so that people can eat closer to home, making it much faster.
2. Non-Filing CDN VS Domestic CDN: What’s the difference?
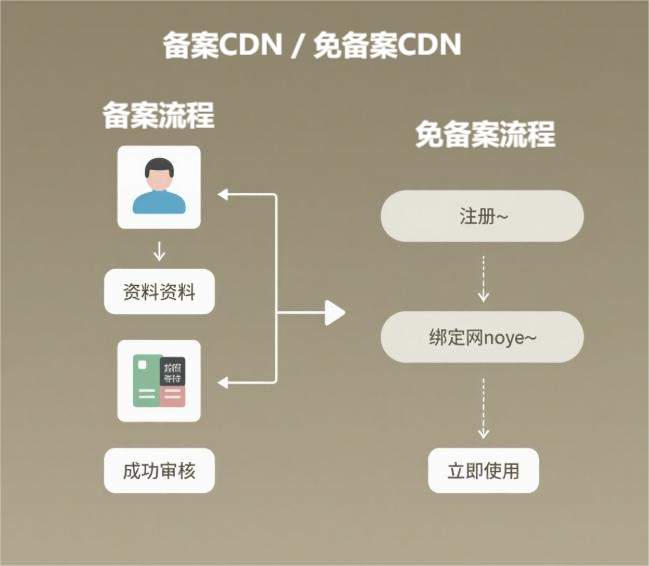
Below, we will clarify each difference one by one.
1. Biggest Difference: Do You Need to Register?
✅ Domestic CDN: Domain must be registered in China
To use a CDN in mainland China, like Alibaba Cloud or Tencent Cloud’s CDN, your website’s domain must go through ICP Registration. This is required by Chinese law, meaning your website needs to be "registered."
The registration process can take 1 to 3 weeks and is quite cumbersome, requiring you to fill out information about the hosting organization, website details, and sometimes even take photos of the backdrop.
✅ Non-Filing CDN: No need for registration
You can use international domains like .com, .net, .xyz and connect directly to Non-Filing CDN without any domestic qualifications. You don’t need to report it to the Chinese Ministry of Industry and Information Technology. These types of CDNs are usually deployed outside of mainland China, such as in Hong Kong, Singapore, Japan, the United States, etc.
To summarize in one sentence: Non-Filing CDN is a CDN "not subject to Chinese regulation."
2. Node Deployment Locations
- Domestic CDN nodes are mainly concentrated in various provinces of mainland China, close to users, resulting in very fast access speeds.
- Non-Filing CDN nodes are mainly located outside of mainland China, close to regions like Hong Kong, Taiwan, Singapore, and overseas Chinese areas.
That means, if your main users are in mainland China, domestic CDN is definitely faster; but if your users are global or if your website faces the risk of being blocked in mainland China, Non-Filing CDN is more advantageous.
3. Connection Methods and Access Barriers
- Domestic CDN: Requires domain binding and ICP number upload. Some platforms may even require you to verify your ID or business information, making it suitable for certified official websites.
- Non-Filing CDN: More flexible connection; you can simply point your domain to the CDN. It is suitable for startup websites, temporary projects, gray area projects, or foreign services.
4. Review Mechanism Differences
- Domestic CDN automatically cooperates with content review systems, such as keyword filtering and blocking illegal content. If your website content is "non-compliant," it may be forcibly taken offline.
- Non-Filing CDN generally has a more relaxed review process, making it more suitable for websites with high content freedom requirements, such as overseas news, forums, financial platforms, cryptocurrency, game accelerators, etc.
5. Resistance to Blocking

If your website has "wall" sensitive content or is likely to be blocked (such as Telegram mirror sites, VPN promotion pages, cryptocurrency wallets), a domestic CDN will not be accessible.
Non-Filing CDN can combine technologies such as intelligent routing + IP rotation + international BGP + DNS intelligent resolution to bypass the Great Firewall and increase availability.
3. Why do so many people choose Non-Filing CDN?
Here are a few practical reasons explaining why Non-Filing CDN is becoming increasingly popular.
1. Registration is too troublesome, especially for individuals or startup projects
Many people just want to test a project, create a temporary activity page, or set up a small site without dealing with the hassle of registration and photo-taking. Non-Filing CDN allows instant use and can be online in a few minutes.
2. Working on foreign markets without Chinese traffic
For example, if you’re doing cross-border e-commerce, overseas marketing, or running an English blog, and you don’t want domestic users to access it, then registration is a burden. Non-Filing CDN is the right choice.
3. Content is likely to be blocked or you don’t want restrictions
For websites like private game servers, movie sites, blockchain, adult content, or web novel sites, content may be immediately scrutinized if hosted on domestic CDNs. Non-Filing CDN provides better "privacy space."
4. Does Non-Filing CDN have no drawbacks?
Of course, it has some drawbacks. Here are a few things to keep in mind:
1. Speed is not as fast in mainland China as domestic CDN
After all, the physical nodes are not in mainland China, which still causes some network delay, especially during peak hours when there may be slight buffering.
2. The risk of being "blocked" still exists
Although Non-Filing CDN is more resistant to blocking compared to direct servers, if technologies like IP rotation, domain distribution, SNI encryption, and DNS pollution protection are not implemented, there is still a risk of being blocked.
3. Some operators may limit speed
Some of China’s major telecom operators limit the speed of international traffic. For example, if you use a Non-Filing CDN with a Hong Kong node, there may sometimes be interruptions or speed throttling.
5. Real-world usage examples: Which one is right for whom?
| User Type | Recommended CDN Type | Reason |
|---|---|---|
| Domestic formal enterprise websites, e-commerce | Domestic CDN | Fast, secure, compliant |
| Startup websites, temporary projects | Non-Filing CDN | Quick launch, low barriers |
| Overseas Chinese community / Chinese forums | Non-Filing CDN | Global reach, bypasses registration |
| VPN promotion, cryptocurrency wallet | Non-Filing CDN | High flexibility, anti-blocking |
| Domestic government and enterprise sites | Domestic CDN | Must register, meets regulatory requirements |
6. Technical comparison summary table
| Item | Domestic CDN | Non-Filing CDN |
|---|---|---|
| Does it require registration? | ✅ Yes | ❌ No |
| Node Locations | Mainly in mainland China | Mainly overseas |
| Access Speed | Fast in mainland China | Fast overseas, slightly slower in China |
| Content Review | Strict | Loose |
| Anti-blocking ability | Weak | Strong |
7. How to choose a reliable Non-Filing CDN provider?
When selecting a Non-Filing CDN, keep these factors in mind:
- Node Quality: Does it have nodes in places like Hong Kong, Japan, Singapore, the United States, etc.? Does it support BGP and multi-line access?
- Anti-blocking Mechanisms: Does it support IP rotation, domain rotation, DNS intelligent resolution, TLS obfuscation, etc.?
- Stability: Does it provide SLA service guarantees? Is there real-time monitoring?
- After-sales Support: Does it have dedicated customer support, a Telegram technical group, and a ticket system?
- Payment Methods: Does it support multiple payment methods like USDT, Alipay, PayPal, etc.?
Recommended brands include: 08Host High Defense CDN, CDN07, etc.
8. Choosing the right CDN is choosing your website’s lifeline
Whether you're working on a formal project or exploring freely, the choice of CDN is the foundation for your website's stability.
Choose domestic CDN for speed and compliance; choose Non-Filing CDN for flexibility and freedom. Both have their advantages, and it’s not about one being better than the other, but rather—the best choice is what suits you.
Share this post:
Related Posts

Hong Kong High-Defense CDN Recommendations (2026 Latest Edition)
Not all Hong Kong high-defense CDNs can withstand attacks. This article compares the protection stre...
No-ICP CDN Recommendations | Which Ones Actually Speed Up Mainland China AND Can Withstand Attacks?
How to choose a no-ICP CDN? Based on real webmaster tests, this article compares multiple CDN provid...
What's the Difference Between DDoS-Protected CDN and DDoS-Protected IP? A Clear Guide to Help You Choose.
What's the difference between a DDoS-protected CDN and a DDoS-protected IP? Which one should your we...
